-- PedroRio - 14 Dec 2010
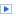
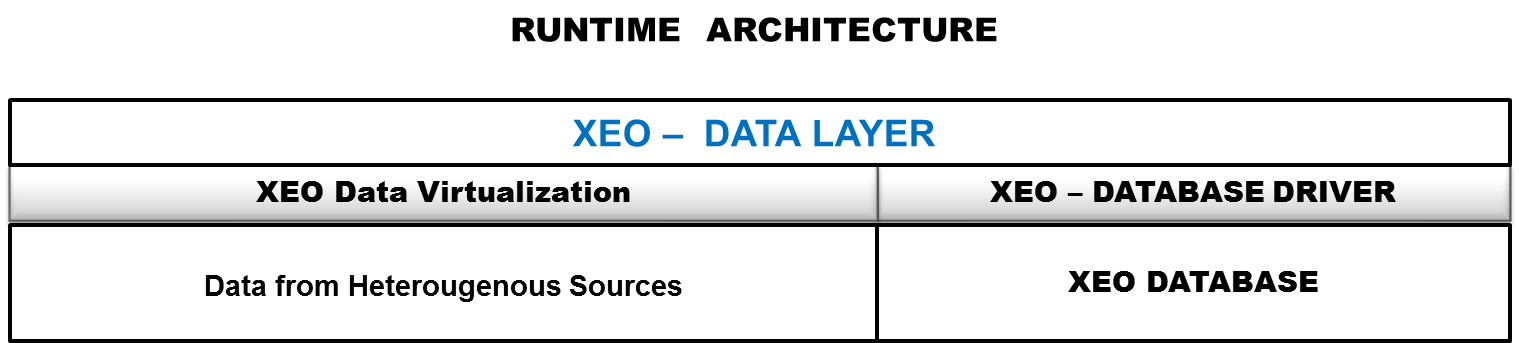 Figure Arch.1 - XEO Architecture, only including its Data Layer
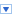
In the second layer, XEO Core System, you find the XEO Engine. The XEO is responsible for all the abstractions seen in the XEO Concepts section, as well as some other features, such as XEOQL (XEO Query Language), which is a SQL-esque language used in XEO to query instances of XEO Models, or the XEO Java API which is the primary method of defining custom behavior for XEO Models. The XEO Core System layer is depicted in figure Arch.2, bellow. Even in runtime, XEO Models are grouped in XEO Packages (again, merely a logical grouping).
Figure Arch.1 - XEO Architecture, only including its Data Layer
In the second layer, XEO Core System, you find the XEO Engine. The XEO is responsible for all the abstractions seen in the XEO Concepts section, as well as some other features, such as XEOQL (XEO Query Language), which is a SQL-esque language used in XEO to query instances of XEO Models, or the XEO Java API which is the primary method of defining custom behavior for XEO Models. The XEO Core System layer is depicted in figure Arch.2, bellow. Even in runtime, XEO Models are grouped in XEO Packages (again, merely a logical grouping).
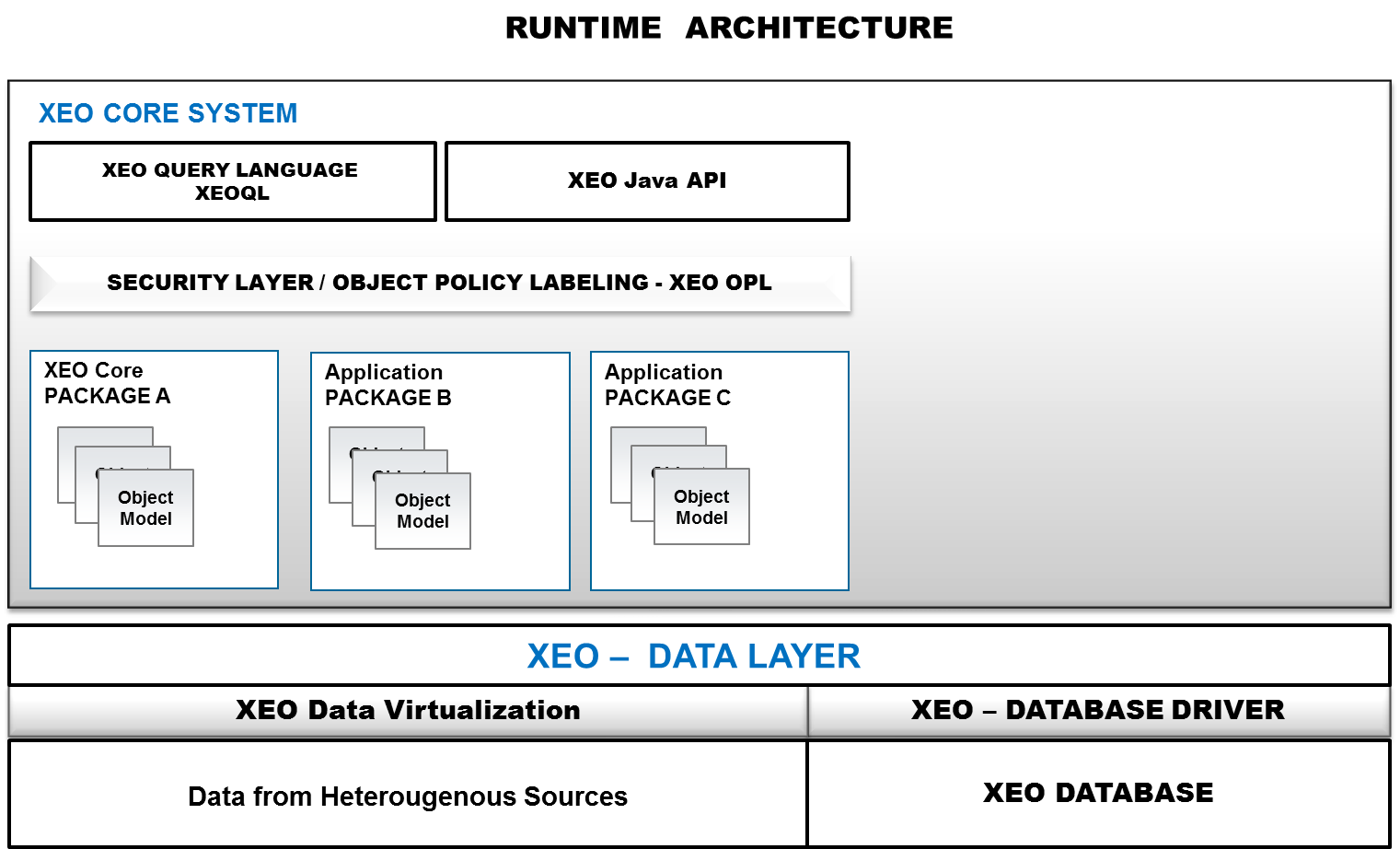 Figure Arch.2 - XEO Architecture with Data Layer and Core System Layer
Above XEO's Core System Layer is the XEO Client Layer, which deals with the rendering of web-pages for user interaction. XEO Web Components have built-in security mechanisms, which allow to create rules where users may or may not see certain components in a given viewer (or see a viewer altogether). The XEO Client Controller Layer is depicted in figure Arch.3.
Figure Arch.2 - XEO Architecture with Data Layer and Core System Layer
Above XEO's Core System Layer is the XEO Client Layer, which deals with the rendering of web-pages for user interaction. XEO Web Components have built-in security mechanisms, which allow to create rules where users may or may not see certain components in a given viewer (or see a viewer altogether). The XEO Client Controller Layer is depicted in figure Arch.3.
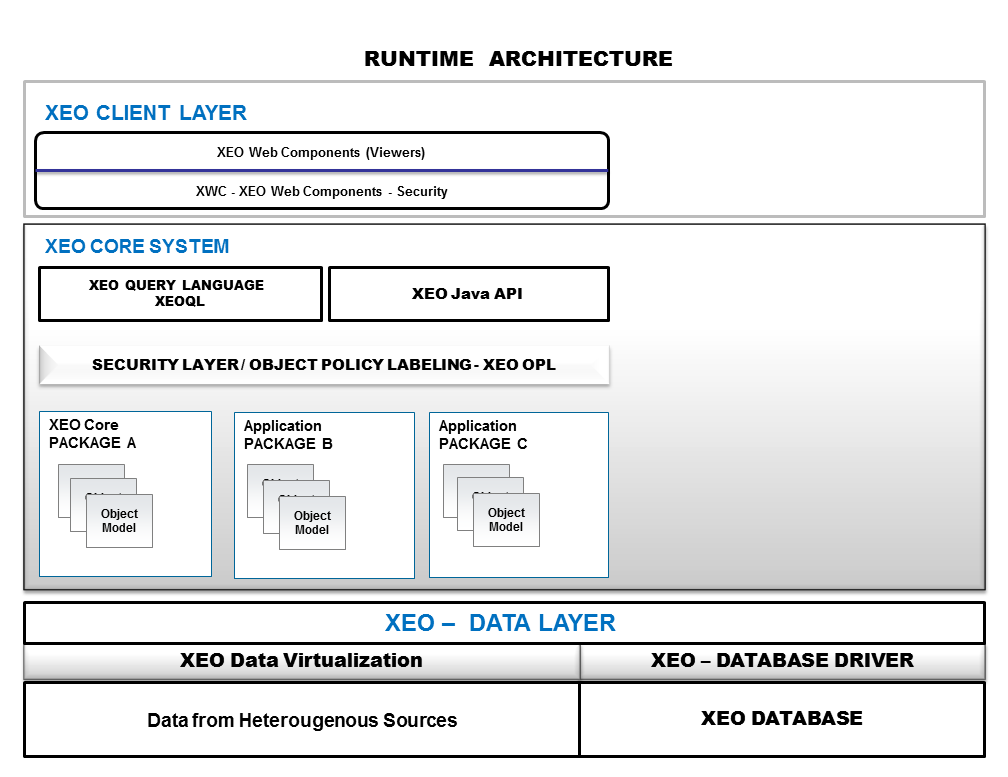 Figure Arch.3 - XEO Data Layer, Core System Layer with the added Client Layer
The XEO Framework not only allows for great customization of its XEO Models, has querying and security mechanisms (as well as a web layer) but can also be extended with the concept of a XEO Module. A XEO Module is a way of adding new features to XEO (which can be installed separately from the main framework). A XEO Module may define a set of XEO Models, have its own API, include existing Java libraries and interact with XEO's Java API to create the desired features. Presently, the XEO framework has been extended with two modules, one to allow interaction with XEO Model instances via web services (REST and SOAP) and one to integrate with a Business Process Management (BPM) engine. The ability to interact directly with XEO's Java API allows for modules to integrate in the Core System Layer, Data Layer or the Client Layer, as depicted in figure Arch.4
Figure Arch.3 - XEO Data Layer, Core System Layer with the added Client Layer
The XEO Framework not only allows for great customization of its XEO Models, has querying and security mechanisms (as well as a web layer) but can also be extended with the concept of a XEO Module. A XEO Module is a way of adding new features to XEO (which can be installed separately from the main framework). A XEO Module may define a set of XEO Models, have its own API, include existing Java libraries and interact with XEO's Java API to create the desired features. Presently, the XEO framework has been extended with two modules, one to allow interaction with XEO Model instances via web services (REST and SOAP) and one to integrate with a Business Process Management (BPM) engine. The ability to interact directly with XEO's Java API allows for modules to integrate in the Core System Layer, Data Layer or the Client Layer, as depicted in figure Arch.4
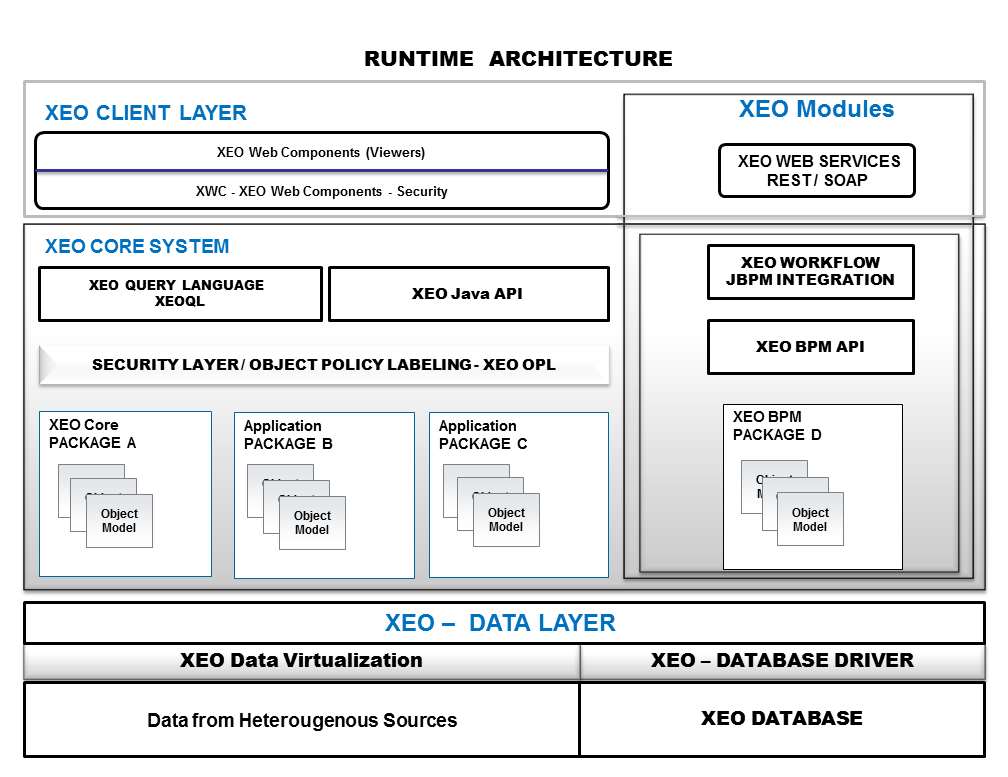 Figure Arch.4 - Complete XEO Runtime Architecture
In the next chapter we'll describe a sample application (which we'll use throughout the documentation, building an incrementally complex application), read more.
_
Figure Arch.4 - Complete XEO Runtime Architecture
In the next chapter we'll describe a sample application (which we'll use throughout the documentation, building an incrementally complex application), read more.
_
XEO Architecture
XEO is a Java framework and XEO Applications are deployed in a J2EE Application Server (such as JBOSS, GlashFish). XEO's Architecture will be explained by layers (with a complete overview at the end). XEO is structured in three horizontal layers, which are set upon each other. The layers are XEO Data Layer, XEO Core System and XEO Client Controller Layer. XEO's Data Layer, depicted in figure Arch.1, has two components. The Database Driver component and the component. The Database Driver is the connection to the DBMS where instances of XEO Object Models are to be saved while the Virtualization layer (at the time of writing not fully implemented) is the component which allows the use of other data sources (such as web services, XML databases, LDAP, etc..) for object instances. Figure Arch.1 - XEO Architecture, only including its Data Layer
In the second layer, XEO Core System, you find the XEO Engine. The XEO is responsible for all the abstractions seen in the XEO Concepts section, as well as some other features, such as XEOQL (XEO Query Language), which is a SQL-esque language used in XEO to query instances of XEO Models, or the XEO Java API which is the primary method of defining custom behavior for XEO Models. The XEO Core System layer is depicted in figure Arch.2, bellow. Even in runtime, XEO Models are grouped in XEO Packages (again, merely a logical grouping).
Figure Arch.1 - XEO Architecture, only including its Data Layer
In the second layer, XEO Core System, you find the XEO Engine. The XEO is responsible for all the abstractions seen in the XEO Concepts section, as well as some other features, such as XEOQL (XEO Query Language), which is a SQL-esque language used in XEO to query instances of XEO Models, or the XEO Java API which is the primary method of defining custom behavior for XEO Models. The XEO Core System layer is depicted in figure Arch.2, bellow. Even in runtime, XEO Models are grouped in XEO Packages (again, merely a logical grouping).
 Figure Arch.2 - XEO Architecture with Data Layer and Core System Layer
Above XEO's Core System Layer is the XEO Client Layer, which deals with the rendering of web-pages for user interaction. XEO Web Components have built-in security mechanisms, which allow to create rules where users may or may not see certain components in a given viewer (or see a viewer altogether). The XEO Client Controller Layer is depicted in figure Arch.3.
Figure Arch.2 - XEO Architecture with Data Layer and Core System Layer
Above XEO's Core System Layer is the XEO Client Layer, which deals with the rendering of web-pages for user interaction. XEO Web Components have built-in security mechanisms, which allow to create rules where users may or may not see certain components in a given viewer (or see a viewer altogether). The XEO Client Controller Layer is depicted in figure Arch.3.
 Figure Arch.3 - XEO Data Layer, Core System Layer with the added Client Layer
The XEO Framework not only allows for great customization of its XEO Models, has querying and security mechanisms (as well as a web layer) but can also be extended with the concept of a XEO Module. A XEO Module is a way of adding new features to XEO (which can be installed separately from the main framework). A XEO Module may define a set of XEO Models, have its own API, include existing Java libraries and interact with XEO's Java API to create the desired features. Presently, the XEO framework has been extended with two modules, one to allow interaction with XEO Model instances via web services (REST and SOAP) and one to integrate with a Business Process Management (BPM) engine. The ability to interact directly with XEO's Java API allows for modules to integrate in the Core System Layer, Data Layer or the Client Layer, as depicted in figure Arch.4
Figure Arch.3 - XEO Data Layer, Core System Layer with the added Client Layer
The XEO Framework not only allows for great customization of its XEO Models, has querying and security mechanisms (as well as a web layer) but can also be extended with the concept of a XEO Module. A XEO Module is a way of adding new features to XEO (which can be installed separately from the main framework). A XEO Module may define a set of XEO Models, have its own API, include existing Java libraries and interact with XEO's Java API to create the desired features. Presently, the XEO framework has been extended with two modules, one to allow interaction with XEO Model instances via web services (REST and SOAP) and one to integrate with a Business Process Management (BPM) engine. The ability to interact directly with XEO's Java API allows for modules to integrate in the Core System Layer, Data Layer or the Client Layer, as depicted in figure Arch.4
 Figure Arch.4 - Complete XEO Runtime Architecture
In the next chapter we'll describe a sample application (which we'll use throughout the documentation, building an incrementally complex application), read more.
_
Figure Arch.4 - Complete XEO Runtime Architecture
In the next chapter we'll describe a sample application (which we'll use throughout the documentation, building an incrementally complex application), read more.
_ | I | Attachment | Action | Size | Date | Who | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
Architechture1.png | manage | 19.8 K | 2011-03-18 - 09:31 | PedroRio | |
| |
Architechture2.png | manage | 50.3 K | 2011-03-18 - 09:32 | PedroRio | |
| |
Architechture3.png | manage | 34.7 K | 2010-12-14 - 14:44 | PedroRio | XEO Client Layer |
| |
Architechture4.png | manage | 49.0 K | 2010-12-14 - 14:50 | PedroRio | XEO Modules |
Topic revision: r5 - 2011-04-04 - NicolauGrosskopf
XEO Primer
- - Instalation
- - Introduction
- - Concepts
- - Architecture
- - XEO Library
- - Deploy to EAR
- - PreferenceStore
- - XEO Model Reference
- - Security
- - Java API
- - BOL
- - XEOQL (BOQL)
- - Administrating
- - Background Tasks
- - boConfig.xml
- - Web.xml
- - Known Issues
- - XEO Flags
- - Web Components
- - Java Samples
- - Custom Components
- - Component Plugins
- - Internationalization
- - Viewer Events
- - Value Change Listeners
- - XUIServlet
- - XeoLocalization
- - XvwTemplates
No permission to view TWiki.WebTopBar