-- PedroRio - 21 Dec 2010
Car ( Car )
Brand ( Brand )
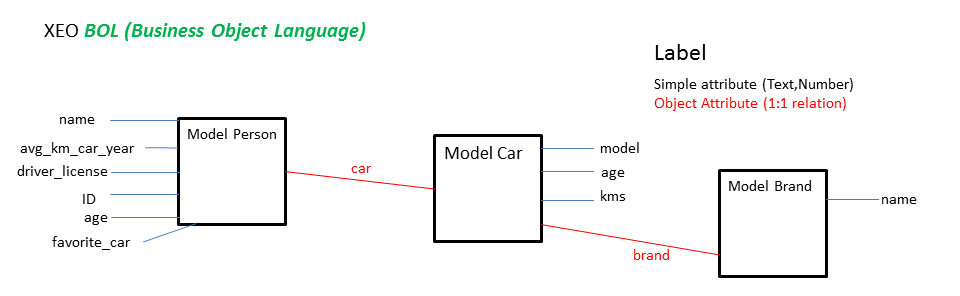 Figure BOL.1 - XEO Models for the BOL example.
Tentar verificar se é possível usar "parent.att" em BOL
Figure BOL.1 - XEO Models for the BOL example.
Tentar verificar se é possível usar "parent.att" em BOL
ROUND ROUND(Number) - Rounds to the nearest integer (0.4 -> 0; 0.5 -> 1)
CONCAT (Concatenates two values)
TO_DATE (Converts to a Date value)
SUM
SUBTRACT
DIFF_IN_DAYS (Difference in days between two dates) Returns the number of days between two dates
DIFF_IN_UTIL_DAYS (Difference in work days between two dates)
IS_NULL (Checks if a given value is null) Works for all kinds of attributes except for Collection attributes. Returns true is the value of the attribute is null (i.e. newly created object will have all attributes null (except if they have a default value)). Example:
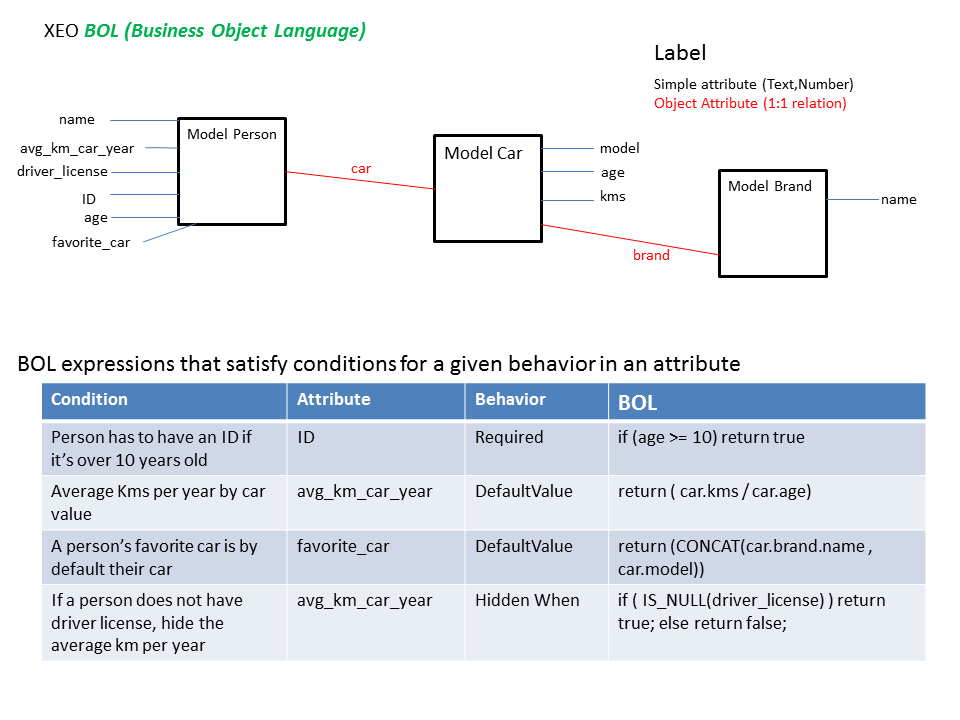 Figure BOL.2 - Examples of BOL Expressions
_
Figure BOL.2 - Examples of BOL Expressions
_
Business Object Language (BOL)
The Business Object Language is a small expression language to help define conditions for the behavior in XEO Object Models. It allows to reference attribute values, compare them with other values as well as making small calculations. The following sections explain the various operators and statements that can be used in the language.Attributes
XEO Model attributes can be referenced in BOL expressions by their name, for example if you want to create an expression that represents the following ideia: "If the value of attribute X is bigger than 5, return true" the bol expression would be "if (x > 5) return true". This syntax works for attributes that are not Collection nor Object. When dealing with a XEO Model attribute you can refer to the values of its attributes by using the separator '.' ; Imagine a situation where we have a XEO Model to represent a Person, a Car and a Car Brand, where Person has 1:1 relation to Car which has a 1:1 relation to Brand, those relations are depicted in figure BOL.1. The following tables have the definition of the Object Models. Person ( Person )| Attribute Name | Attribute Type | Label | Description | Length | Required | Object Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| name | Text | Name | Person Name | 30 | - | N/A |
| avg_km_car_year | Number | Average Km's | Average KM's per year with a car | 30 | - | N/A |
| driver_license | Text | Driver License Number | The identifier of the driver license | 30 | - | N/A |
| ID | Text | Identifier | The identifier of the person | 30 | - | N/A |
| age | Number | Age | The age of the person | 3 | - | N/A |
| favorite_car | Text | Favorite Car | The favorite car of the person | 30 | - | N/A |
| car | Object | Car | The car of the person | 30 | - | Car |
| Attribute Name | Attribute Type | Label | Description | Length | Required | Object Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| model | Text | Model | The model of the car | 30 | - | N/A |
| age | Number | Age | The age of the car | 3 | - | N/A |
| kms | Number | Kilometers | The number of kilometers the car has done | 4 | - | N/A |
| brand | Object | Brand | The car brand | 4 | - | N/A |
| Attribute Name | Attribute Type | Label | Description | Length | Required | Object Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| name | Text | Name | Name of the category | 30 | true | N/A |
 Figure BOL.1 - XEO Models for the BOL example.
Tentar verificar se é possível usar "parent.att" em BOL
Figure BOL.1 - XEO Models for the BOL example.
Tentar verificar se é possível usar "parent.att" em BOL 
Boolean Values
Boolean values can be used in BOL expressions. The folowing expressions represent the "true" value:- true
- yes
- y
- YES
- false
- no
- n
- NO
Conditional Statements
In BOL you can use conditional expressions in the form of if/else statements. The syntax is like the following:if ( CONDITION ) BOL EXPRESSION else BOL EXPRESSIONIf you need more conditions you use if/else statements with brackets
if (CONDITION ){
//BOL EXPRESSIONS
//BOL EXPRESSIONS
} else {
//BOL EXPRESSIONS
//BOL EXPRESSIONS
}
_
Returning a value
Most BOL expressions are used in places where they must return a value (be it a boolean, string or numeric value). In order to do that BOL has the expression "return" which will return the result of evaluating the expression on its right side. Example:return true
return YES --- if (age > 18) return "You can drive" else return "Need to wait a little longer"
Operators
BOL expressions can have multiple operands linked by operators (as with most programming languages). In BOL the following operators are allowed:- > (Bigger)
- >= (Bigger or Equal)
- == (Equal)
- <= (Less or Equal)
- < (Less)
- ! (Negation)
- && ( And)
- || (Or)
- ! = (Different)
_if (att1 > 2 && att2 != 45 && att3 == 'F') return "42"
Functions
BOL includes a set of predefined functions which can be used inside every BOL Expression. DATE FUNCTIONS NOW - Returns the current date with time TODAY - Returns the current date without time information NOW_HOURS - Returns the current date with time information about the hour (discards minutes, seconds and mili-seconds) NOW_MINUTES - Returns the current date with time information about the hour and minutes (discards seconds and mili-seconds)ROUND ROUND(Number) - Rounds to the nearest integer (0.4 -> 0; 0.5 -> 1)
CONCAT (Concatenates two values)
- CONCAT(String,String)
- CONCAT (Number,Number) - Number can be long/int value
- CONCAT (Object,Object) - Converts each Object to string and concatenates
TO_DATE (Converts to a Date value)
- TO_DATE(Date, Format)
- TO_DATE (Object, Format), Object is converted to a String and converted to date
- TO_DATE (long, Format) - Convertes UNIX time miliseconds to a date
SUM
- SUM ( Number , Number )
- SUM (Object , Object) - Converts the Object to Numbers and sums the numbers
Sum(3 , 1 ) will return 4 Sum (att1, att2 ) - assuming both are attributes which contain a value that can converted to a number will return the sum of the two
SUBTRACT
- SUBTRACT (Number, Number)
- SUBTRACT (Object, Object) - Converts the Object to String
Substract (3 , 1 ) will return 2 Subtract (att1, att2 ) - assuming both are attributes which contain a value that can converted to a number will return the difference between the two
DIFF_IN_DAYS (Difference in days between two dates) Returns the number of days between two dates
- DIFF_IN_DAYS (Date, Date)
- DIFF_IN_DAY (Date, Long)
- DIFF_IN_DAY (Long, Date)
- DIFF_IN_DAY (Long, Long)
DIFF_IN_DAYS (NOW, TO_DATE('22/12/2012','dd/MM/yyyy')) which will return the number of days between today and December 22nd, 2012 DIFF_IN_DAYS (TO_DATE('20/12/2012','dd/MM/yyyy'), TO_DATE('22/12/2012','dd/MM/yyyy')) which will return 2 (two)
DIFF_IN_UTIL_DAYS (Difference in work days between two dates)
- DIFF_IN_UTIL_DAYS (Date, Date)
- DIFF_IN_UTIL_DAYS (Date, Long) - The long value is a Unix timestamp
- DIFF_IN_UTIL_DAYS (Long, Date) - The long value is a Unix timestamp
- DIFF_IN_UTIL_DAYS (Long, Long) - The long value is a Unix timestamp
IS_NULL (Checks if a given value is null) Works for all kinds of attributes except for Collection attributes. Returns true is the value of the attribute is null (i.e. newly created object will have all attributes null (except if they have a default value)). Example:
if (IS_NULL (att1)) return true_
Examples
This section shows some examples of BOL expressions using the previous Model (Person, Car and Brand) Figure BOL.2 - Examples of BOL Expressions
_
Figure BOL.2 - Examples of BOL Expressions
_ Topic revision: r12 - 2011-04-04 - NicolauGrosskopf
XEO Primer
- - Instalation
- - Introduction
- - Concepts
- - Architecture
- - XEO Library
- - Deploy to EAR
- - PreferenceStore
- - XEO Model Reference
- - Security
- - Java API
- - BOL
- - XEOQL (BOQL)
- - Administrating
- - Background Tasks
- - boConfig.xml
- - Web.xml
- - Known Issues
- - XEO Flags
- - Web Components
- - Java Samples
- - Custom Components
- - Component Plugins
- - Internationalization
- - Viewer Events
- - Value Change Listeners
- - XUIServlet
- - XeoLocalization
- - XvwTemplates
No permission to view TWiki.WebTopBar