-- PedroRio - 27 Dec 2010
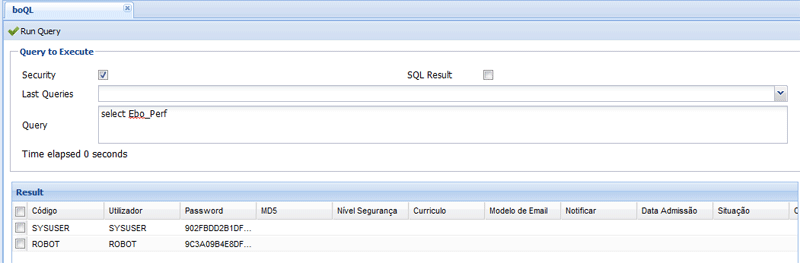 Figure XEOQL.1 - Executing a simple query in the XEOQL console.
In the bottom of figure XEOQL.1 you can see the two instances of Ebo_Perf (a default XEO application has the SYSUSER and ROBOT user) that are the result of this query. The results reflect a default XEO application. See in the following section how to select instances which are related to a current instance (through collection or object attributes). It's possible to select instances which are related with other instances (through a object or collection attribute), see the "dot syntax" section bellow for more information.
Figure XEOQL.1 - Executing a simple query in the XEOQL console.
In the bottom of figure XEOQL.1 you can see the two instances of Ebo_Perf (a default XEO application has the SYSUSER and ROBOT user) that are the result of this query. The results reflect a default XEO application. See in the following section how to select instances which are related to a current instance (through collection or object attributes). It's possible to select instances which are related with other instances (through a object or collection attribute), see the "dot syntax" section bellow for more information.
___
Contains Clause
The contains clause allows you to search for instances of XEO Models which have a certain keyword indexed by Ebo_TextIndex (Full text search indexer). If you know you have instances of Object Model "Foo" that have a certain attribute with the word "bar" you can search for those instances by using the following query:
Table XEOQL.1 - Special constants in XEOQL
_
XeoQL - XEO Query Language ( also known as BOQL )
XEO Query Language (XEOQL a.k.a BOQL - Business Object Query Language) is a language designed to query instances of XEO Object Models. It's very similar to SQL and has many of the same constructors. SQL is designed to return records from a relational database, while XEOQL is designed to return Object Model instances from its datasource (typically a relational database). Using XEO's Java API to issue a XEOQL expression against the datasource will produce a boObjectList instance which can be used to iterate through all elements that are the result of the query. The methods available in ObjectListManager allow you to create a boObjectList instance from a XEOQL query. The syntax for a XEOQL expression is the following: SELECT [MY] [USING user/pwd] [attlist FROM] objname [WHERE whereStatement (AND | OR whereStament) ][ORDER BY attName[ASC|DESC] (,attName [ASC|DESC])*]* Although the syntax may seem complicated usually you'll not use every option in the syntax. Let's start with the simplest of queries, selecting all instances of a given Object Model, for example the system Object Model Ebo_Perf (which represents a user).select Ebo_PerfExecuting this query in the XEOQL Console (available in every XEO Application's Administration Viewer) provides the following results:
 Figure XEOQL.1 - Executing a simple query in the XEOQL console.
In the bottom of figure XEOQL.1 you can see the two instances of Ebo_Perf (a default XEO application has the SYSUSER and ROBOT user) that are the result of this query. The results reflect a default XEO application. See in the following section how to select instances which are related to a current instance (through collection or object attributes). It's possible to select instances which are related with other instances (through a object or collection attribute), see the "dot syntax" section bellow for more information.
Figure XEOQL.1 - Executing a simple query in the XEOQL console.
In the bottom of figure XEOQL.1 you can see the two instances of Ebo_Perf (a default XEO application has the SYSUSER and ROBOT user) that are the result of this query. The results reflect a default XEO application. See in the following section how to select instances which are related to a current instance (through collection or object attributes). It's possible to select instances which are related with other instances (through a object or collection attribute), see the "dot syntax" section bellow for more information.
The dot syntax
An Object Model A can define an 1:N relation with another Object Model through a collection attribute (named, for example, attCollection) or a 1:1 relation through an object attribute. It's possible (using XEOQL) to retrieve instances associated with other instances by using a dot syntax. For example: The LIB_Book Object Model (created for the XEO Library) defines a categories attribute (collection attribute) and a publisher attribute (object attribute). To select the publishers that is associated with a book the following query would be needed:select LIB_Book.publisherThe previous query will return a list of all LIB_Publisher instances that are related to a LIB_Book instance (if one wanted only the publisher of a given book, you would need a where clause, which will be discussed in the next section). To select all LIB_BookCategory instances associated to any given book, the following query could be used
select LIB_Book.categoriesYou can go further down the hierarchy, like selecting all publisher nucleus from publishers that are related to book instance with the following query:
select LIB_Book.publisher.nucleusDot syntax can be used continually as long as the attributes being selected are of type object or collection.
Where Clause
In order to restrict the results of a XEOQL expression, and just like the SQL counterpart, XEOQL provides a WHERE clause. The where clause allows to restrict selection by using logical operators, attribute references, functions, arithmetic and literals. The syntax for the where clause is the following:WHERE whereStatement (AND | OR whereStament)*The whereStatament expression encapsulates all the possible combinations for valid expressions which can be created using the following elements:
- Attributes - Reference to an attribute to be compared with some value (ex. Literals)
- Literals - Literal values to be used for comparison
- Functions
- Arithmetic Operator - Allow to make calculations using +,-,*,/ (i.e sum, subtraction, multiplication and divison)
- Aggregate Functions - Sum(), Avg(), etc...
- Relational operators - (
, >, <, >, <=, like, is null, etc...)
Where Clause - Attributes (and the Dot Syntax)
In a XEOQL expression is possible to retrict the selected instances by making to only instances whose attributes match a certain condition are returned. Recall from the XEO Library introduction that the LIB_Book Model had a title attribute (a textual attribute). In order to select all book instances which have a particular title ("Da Vinci Code", for example), we would use the following XEOQL expression.select LIB_Book where title = 'Da Vinci Code'One could also explicitly refer the Object Model being selected in the expression, like the following:
select LIB_Book where LIB_Book.title = 'Da Vinci Code'One can use attributes from instances with which the first is related, for example to select all books which were published by "Wrox".
select LIB_Book WHERE LIB_Book.publisher.name = 'Wrox'or
select LIB_Book WHERE publisher.name = 'Wrox'Beware that when selecting object instances through an attribute (i.e. selecting LIB_Publisher instances by using LIB_Book.publisher) the context for the where clause is that of the of the first Object Model. So if you make the following (wrong) query to select all publishers with a name similar to "Wrox" that have a book published it will fail with an error:
select LIB_Book.publisher where name Like '%Wrox%'The error generated from the query is the following:
QLParser:XEO.QL:null Base Error:Not a valid attribute select LIB_book.publisher where<strong>[name]</strong> Like '%Wrox%'The error occurs because, although the publisher (of the LIB_Publisher Object Model) has an attribute name, in BOQL the context for the where clause is always that of the first Object Model selected, in this case, LIB_Book. In order to make this query correct you would have to refer to the publisher name by prefixing it with "publisher." so that the XEOQL Parser knows that the "name" attribute is from the publisher and not from the book. The correct query would be the following:
select LIB_Book.publisher where publisher.name like '%Wrox%'Another important issue is when comparing to an attribute that is relation. The following two queries are equivalent:
select LIB_Book.publisher where publisher.boui = 111111 select LIB_Book.publisher where publisher = 111111When comparing to a relation attribute you're comparing with its BOUI attribute. _
Where Clause - Literals
In a where clause, often you want to compare certain attribute values with literal values. Such as knowing if a given attributes is bigger than five (5), or a certain attribute represents the date of today. The following table summarizes how to use the various types of literals available.| Literal Type | Usage | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| String | 'String' | |
| Number | 12345 | |
| Duration | 12345 | |
| Date | to_date('5/5/2010','DD-MM-YYYY') | When comparing dates, it's required to use the to_date function, which will converted the date to the internal representation of the database |
Where Clause - Functions
It's possible to user SQL functions directly from whithin a XEOQL expression. The XEOQL parser, however, does not make any type of validation when using these, it passes them directly to the database as SQL.Where Clause - Arithmetic Operators
When refering to a number attribute in a where clause, you can use arithmetic operators build XEOQL expressions, for instance the following query (use of parenthesis to arrange priorities is permited):select LIB_Movement where (fine * 10) / 100 > 200The four arithmetic operators are available (sum, subtraction, mutiplication and division)
Where Clause - Aggregate Functions
It's possible to use aggregate functions in a where clause. Aggregate functions are only usabled with attributes of type number (as they perform calculations on the values of those attributes). There are five aggregate functions that can be used.- AVG - Average of values
- SUM - The sum of values
- COUNT - Count the number of values
- MIN - Minimum value of the group
- MAX - Maximum value of the group
Where Clause - Relational Operators
To compare attributes in a where clause with other values, you'll need the relational operators in XEOQL. There are the following operators:| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| = | Equality operator | 1 = 1 |
| > | Bigger than operator | salary > 1000 |
| < | Less than operator | value < 100 |
| <= | Bigger or equal than operator | salary >= 200 |
| >= | Less or equal than operator | value <= 100 |
| <> | Different operator (not equal) | salary <> 1000 (salary not equal to 1000) |
| ! | Different operator (alias to <>) | salary ! 1000 |
| Like | Allows to compare strings with wildcards | name like "XEO%" name not like "XEO %" |
| Startswith | Restricts attributes that start with a given character | name startswith "A" name startswith "#" |
| In | Retricts arguments to the ones in the following subqueries | boui in (select Object where value > 3) boui not (select Object where value > 3) |
| Is Null | Evaluates if the argument does have a value | Name is null Name is not null |
| Not | Negates a condition | Name not null |
Contains Clause
The contains clause allows you to search for instances of XEO Models which have a certain keyword indexed by Ebo_TextIndex (Full text search indexer). If you know you have instances of Object Model "Foo" that have a certain attribute with the word "bar" you can search for those instances by using the following query:
select Foo where Contains('bar')
You could also use wildcard matching*, such as:
select Foo where Contains('bar%')
which would match Foo instances which have words started with "bar"*.
*Note: Wildcard matching is database dependent. The "contains" clause will be converted to the underlying database's function to make full text searches. In Oracle databases the '%' wildcard can be used in XEOQL expressions (with the contains clause), while Mysql uses the '*' wildcard in its "MATCH" function. When using the contains clause, be sure to read the documentation of your database about wildcard text searching.
Order by Clause
It's possible to order the results of a XEOQL expression by a given attribute or multiple attributes (in ascending or descending order). For example to retrieve all books instances and ordering by title you could use the following expression.select LIB_Book order by title ASC
To select all books instances ordered by the publisher's name and then by title, the following query would do.select LIB_Book order by title DESC
select LIB_Book order by publisher.name,title ASC__
Parameters
When creating a XEOQL expression you can use parameters to bind values. Just like SQL bindings, you can create a XEOQL expression like the following:And later, bind the parameter to a value. To use parameters, the are methods in the ObjectListManager which allow you to pass a XEOQL expression and an array of Objects (the values for the parameters) and will execute your expression with the defined bindings. For example.select LIB_Book where title = ?
EboContext ctx = //get an EboContext
boObjectList results = ObjectListManager.list(ctx, "select LIB_Book where title = ? and ISBN = ?", new Object[] {"Da Vinci Code", 11344444});
__
The MY / USING expressions
The MY expression is used to declare that only instances which were created by the user executing the query should be returned. The USING USER/PASS expression is used to perform queries as another user (using the given username and password, hence the name). If one issues the query:SELECT USING SYSUSER/ABC Ebo_PerfThe results will be all Ebo_Perf instances that the SYSUSER user would see when executing the select Ebo_Perf query.
Special Constants
There are a number of special constants which can be used when creating a XEOQL expression.The following table summarizes them.| Constant | Description |
|---|---|
| CTX_PERFORMER_BOUI | The boui of the user which is executing the query, when you use this in a XEOQL expression it will be automatically replaced by the user's BOUI. |
Sample queries
__
| I | Attachment | Action | Size | Date | Who | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
XEOQL-Console.png | manage | 13.4 K | 2011-01-04 - 17:52 | PedroRio | XEOQL Console - Simple Query |
Topic revision: r18 - 2011-05-04 - NicolauGrosskopf
XEO Primer
- - Instalation
- - Introduction
- - Concepts
- - Architecture
- - XEO Library
- - Deploy to EAR
- - PreferenceStore
- - XEO Model Reference
- - Security
- - Java API
- - BOL
- - XEOQL (BOQL)
- - Administrating
- - Background Tasks
- - boConfig.xml
- - Web.xml
- - Known Issues
- - XEO Flags
- - Web Components
- - Java Samples
- - Custom Components
- - Component Plugins
- - Internationalization
- - Viewer Events
- - Value Change Listeners
- - XUIServlet
- - XeoLocalization
- - XvwTemplates
No permission to view TWiki.WebTopBar